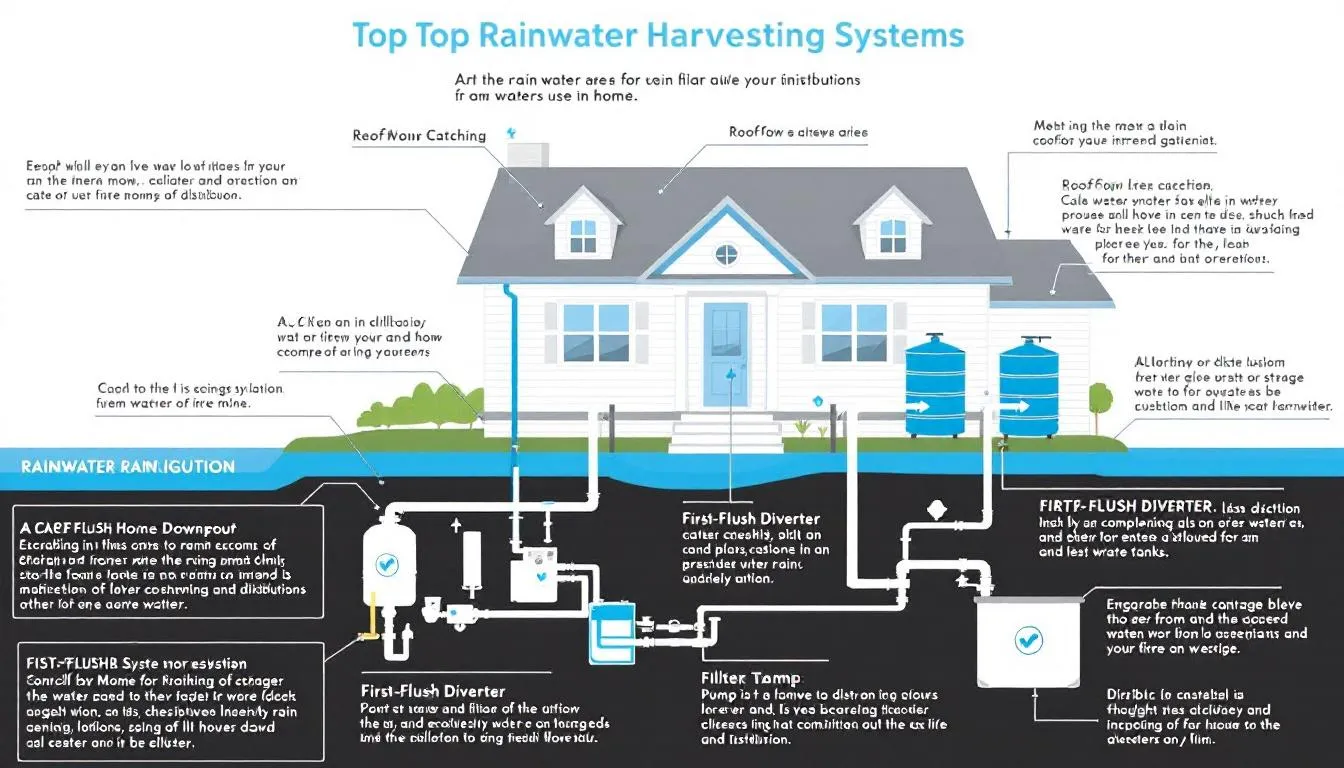
What is Rainwater Harvesting?
Rainwater harvesting is a sustainable solution to water scarcity and environmental conservation. It involves the collection, storage, and reuse of rainwater from rooftops, driveways, and other impervious surfaces. By implementing a rainwater harvesting system, homeowners can reduce their dependence on municipal water supplies, lower their water bills, and contribute to sustainable water management.
This method of storing rainwater is particularly beneficial in urban areas, where excessive stormwater runoff can overwhelm drainage systems, leading to soil erosion and water body contamination. Rainwater harvesting plays a crucial role in conserving natural resources, maintaining the natural water cycle, and mitigating the effects of climate change.
Benefits of Rainwater Harvesting Systems
1. Environmental Benefits
-
Reduces strain on freshwater sources by using harvested rainwater for non-potable purposes such as toilet flushing, landscape irrigation, and washing vehicles.
-
Minimizes stormwater runoff, which helps prevent soil erosion and water pollution.
-
Recharges groundwater table in areas with adequate rainfall, supporting sustainable water management.
-
Decreases urban runoff, preventing contaminants from entering natural water bodies.
2. Economic Benefits
-
Lowers household water bills by reducing reliance on municipal water.
-
Reduces energy savings associated with pumping and treating municipal water supplies.
-
Increases property value for homeowners investing in green infrastructure.
3. Social and Practical Benefits
-
Promotes self-sufficiency by allowing households to manage their own water supply.
-
Encourages community engagement by educating residents about sustainable living.
-
Provides an alternative water source in areas facing water scarcity or unreliable municipal water supplies.
Components of a Rainwater Harvesting System
A typical rainwater collection system consists of several key components that work together to capture rainwater and store it for future use.
1. Catchment Area
-
The catchment area is the surface from which rainwater is collected.
-
In most homes, rooftops serve as the primary collection point.
-
The efficiency of a rainwater collection system depends on:
-
Roof size (measured in square feet).
-
Roof material (smooth surfaces like metal are more efficient than porous materials like clay tiles).
-
Cleanliness to prevent contamination.
-
2. Conveyance System
-
Gutters and downspouts direct the collected rainwater into storage tanks.
-
A first flush diverter helps remove debris, dust, and pollutants before the rainwater enters the storage system.
3. Storage Tanks
-
Rainwater tanks store the harvested water for later use.
-
Tanks can be made from plastic, concrete, fiberglass, or metal.
-
Storage capacity varies based on:
-
Rainfall levels.
-
Intended use of stored water.
-
Available space for tanks.
-
4. Filtration and Treatment System
-
Ensures water quality for its intended purpose.
-
Methods include:
-
Sediment filters for removing debris.
-
Activated carbon filters for eliminating odors and contaminants.
-
Disinfection systems such as UV treatment or chlorination for potable use.
-
5. Distribution System
-
Pump systems supply collected rainwater to designated areas like toilets, irrigation systems, and washing machines.
-
Gravity-fed systems can be used when storage tanks are positioned at a higher elevation.
Types of Rainwater Harvesting
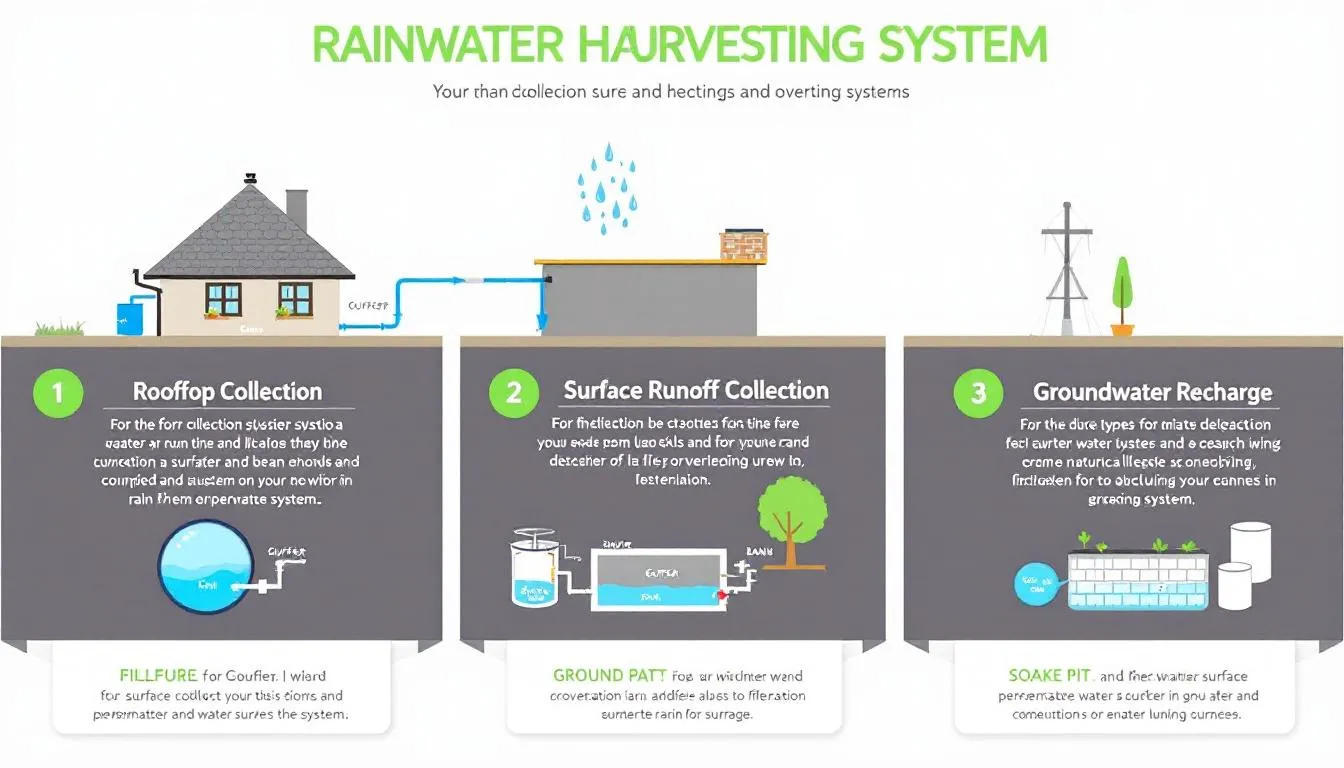
1. Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting
-
Most common method for households.
-
Uses existing structures, reducing the need for additional infrastructure.
-
Ideal for drinking water when properly filtered.
2. Surface Runoff Harvesting
-
Captures stormwater runoff from driveways, gardens, and paved areas.
-
Helps mitigate urban flooding and soil erosion.
-
Often used for landscape irrigation and groundwater recharge.
Implementing a Rainwater Harvesting System
1. Planning and Design Considerations
-
Determine water needs based on household usage.
-
Assess rainfall patterns and catchment area size.
-
Select appropriate storage capacity based on expected rainfall and household demand.
2. Installation Process
-
Install gutters and downspouts to channel rainwater.
-
Position storage tanks in accessible locations.
-
Set up filtration systems and pumps for distribution.
3. Maintenance and Upkeep
-
Regularly clean gutters and filters to prevent blockages.
-
Inspect storage tanks for leaks and contamination.
-
Ensure filtration systems remain functional to maintain water quality.
Using Harvested Rainwater in Homes
|
Usage |
Benefits |
|---|---|
|
Toilet flushing |
Reduces municipal water usage |
|
Garden irrigation |
Provides natural, chemical-free water |
|
Laundry |
Reduces dependency on treated municipal water |
|
Drinking water |
Possible with proper filtration and treatment |
|
Car washing |
Lowers water bills and reduces water waste |
Conclusion

Investing in a rainwater harvesting system is an effective way to achieve sustainable water use at home. Rainwater harvesting plays a crucial role in reducing municipal water demand, conserving natural resources, and mitigating water scarcity.
By implementing harvesting systems, homeowners can:
-
Reduce water bills.
-
Contribute to environmental conservation.
-
Ensure sustainable water management for future generations.
For more information on rainwater harvesting and sustainable living, visit EPA’s Water Conservation Guide and Rainwater Harvesting Guidelines.
https://shorturl.fm/vYaE2
https://shorturl.fm/uWeav